Easy Steps to Set Up Google Tag Manager
Loves Data
Google Tag Manager is a powerful tool that simplifies the process of managing and deploying marketing tags on your website. Whether you're new to digital marketing or looking to streamline your workflow, Google Tag Manager can save you time and effort.
By centralizing your tags, you can easily track user interactions, improve your site’s performance, and make data-driven decisions. So, read on as we explore ways to manage your tags effectively, making your digital marketing efforts more efficient and successful. Let’s get started!
How to Set Up Google Tag Manager in a Few Simple Steps
1. Creating Your Google Tag Manager Container
Creating your Google Tag Manager account is the first step. Start by going to the Google Tag Manager website. Sign in using your Google account. If you don't have a Google account, you will need to create one. This login will be essential for accessing and managing your Tag Manager account.
Once signed in, click on "Create Account." You will be prompted to enter an account name. This name should reflect your business or website. After naming your account, you need to set up a container. A container holds all your tags, triggers, and variables for a specific website or app. Enter a descriptive name for the container and select where you’ll be using it (web, iOS, Android, AMP, or server).
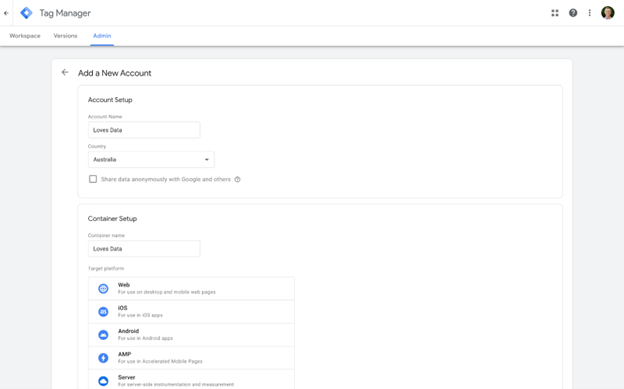
After setting up the container, you’ll receive a piece of JavaScript code. This code is your Tag Manager container snippet. Copy the code and paste it into every page of your website, just after the opening head tag. This will ensure that Google Tag Manager can manage and deploy your tags across your site. Once you’ve added the code, save your changes and return to Tag Manager to start adding tags.
2. Setting Up Your Google Analytics Tag
Inside the container, you'll see options for tags, triggers, and variables. Start by setting up your first tag. Click on the "Tags" section and then "New." Choose a tag type from the list. Common options include the Google Tag for Google Analytics, tags for Google Ads, and custom HTML tags. For instance, if you're setting up a Google Analytics tag, select "Google Tag."
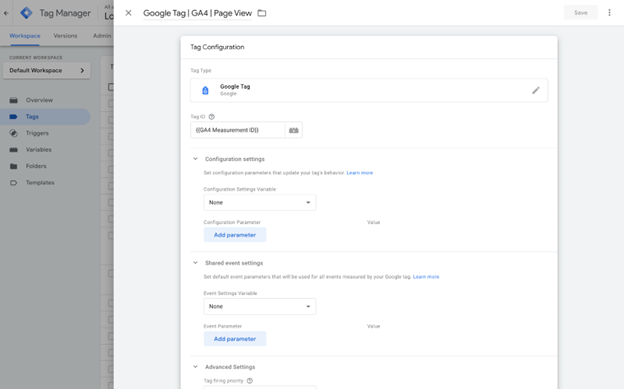
Next, configure your tag settings. Enter your measurement ID, which you can find in your Google Analytics account. Choose the a trigger to define when the tag should fire. For most tags, you will use the "Initialization - All Pages" trigger to capture data from every page on your site.
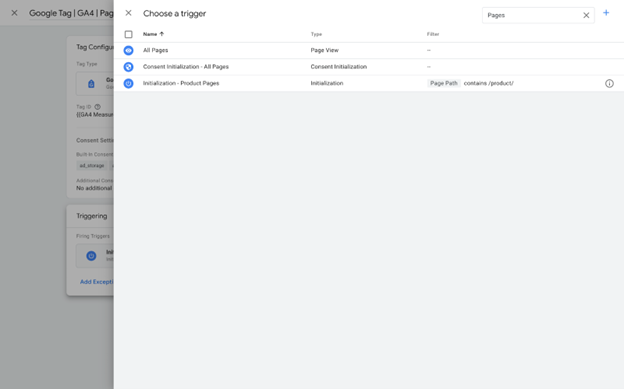
Save your tag and review the summary. Make sure everything looks correct before moving on. Repeat this process for any other tags you wish to add to your container. Properly setting up your container ensures organized and efficient tag management, allowing for accurate data collection and analysis.
3. Adding Additonal Tags to Your Website
Once you have added the Google Tag for Google Analytics, the next step is to add any other necessary tags to your website. If you’re running Google Ads campaigns, you might choose to add a Google Ads conversion tag or remarketing tag using Google Tag Manager. To do this, navigate back to the "Tags" section in Google Tag Manager and click on "New."
Select "Google Ads Conversion Tracking" as the tag type. Next, configure your tag by entering your conversion ID and conversion label from Google Ads. After that, you need to set up a trigger. A trigger tells your tag when to fire. You will want to create a custom trigger to fire the tag for the individual confirmation page or action you want to track as a conversion.
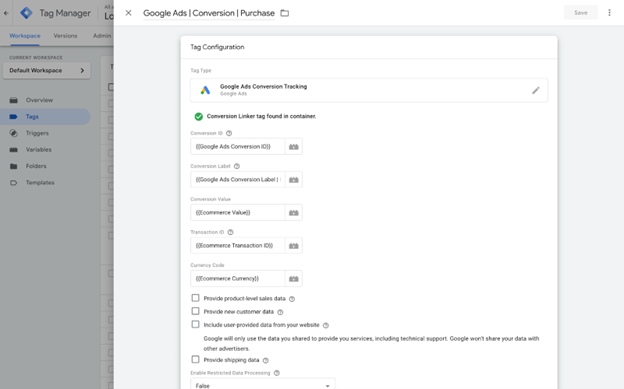
Save your tag and check the summary to ensure everything is configured correctly. Repeat this process for any additional tags you want to add to your container. Adding tags to your website through Google Tag Manager streamlines the process and allows for easier updates and management.
4. Testing and Publishing Your Tags
Before you publish your tags, it's important to test them to make sure they are working correctly. Tag Manager connects to Google Tag Assistant for testing. To access Tag Assistant, click on the "Preview" button in the top right corner of your Tag Manager dashboard.
In Preview mode, navigate to your website. You'll see a debug console at the bottom of the screen showing which tags are firing and when. This helps identify any issues or errors in your tag configuration. Check that all the tags you added are firing as expected. If there are problems, you can troubleshoot by revisiting your tag settings and triggers.
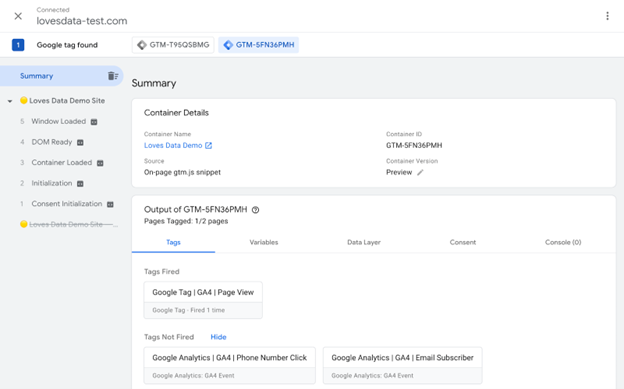
Once you confirm that your tags are working correctly, it’s time to publish them. Exit Preview mode and click on the "Submit" button. You'll be prompted to add a version name and description for your changes, which helps keep track of your updates. Finally, click on "Publish" to make your tags live on your website.
Regularly testing and publishing your tags ensures they work as intended and that you are collecting accurate data. This step is vital for maintaining the integrity of your website analytics.
Setting Up Google Tag Manager
Setting up Google Tag Manager is a straightforward process that can greatly improve your ability to manage tags and track user interactions. Creating your account, setting up your container, adding tags, and testing and publishing them are the key steps to get started. These actions allow you to gather valuable insights and facilitate more effective digital marketing strategies.
By mastering these steps, you can ensure your website collects accurate data, making your marketing efforts more efficient and impactful. Google Tag Manager simplifies tag management, allowing you to focus more on analyzing data and making data-driven decisions.
For those looking for Google Tag Manager training, Loves Data offers expert-led online courses. Enhance your skills and stay ahead in digital marketing by enrolling in our courses today!

Comments