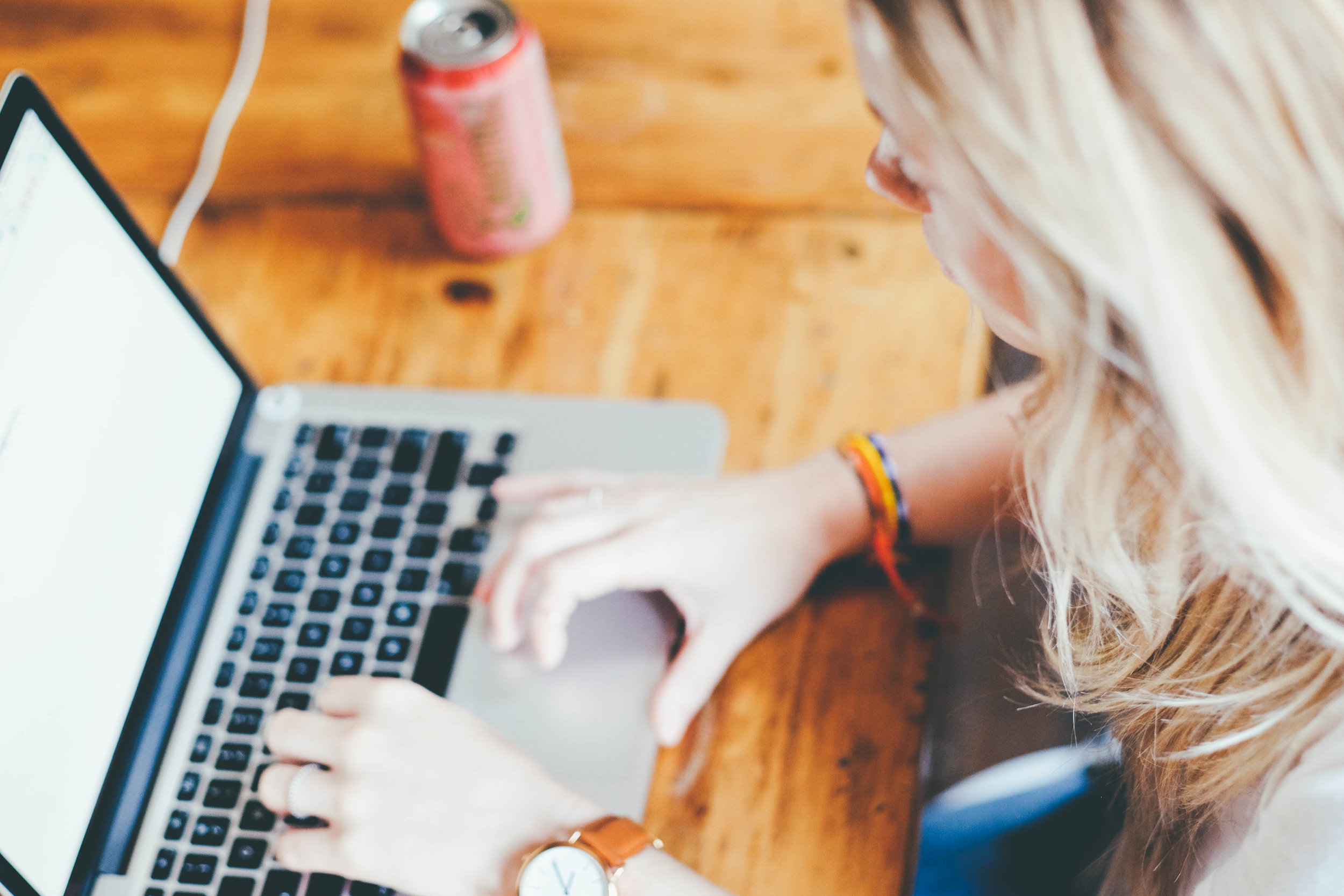
Simple Steps to Set Up Google Tag Manager
Loves Data
Google Tag Manager is a powerful tool that simplifies managing and deploying tags on your website. Tags are small code snippets that track user interactions and send data to platforms like Google Analytics. Adding and updating tags can be time-consuming and error-prone without tag management. Google Tag Manager offers a streamlined way to handle these tags without frequently modifying your website’s code.
Setting up Google Tag Manager is relatively straightforward and can save you time in the long run. Once set up, it allows you to manage all your tags from a single interface, making it easier to implement changes and track performance. This guide walks you through the steps to create your Google Tag Manager account, set up your first container, install the code on your website, and configure your tags.
Whether you are new to digital marketing or looking to refine your tracking methods, Google Tag Manager provides a scalable solution to your website analytics needs. By following these simple steps, you’ll be well on your way to mastering Google Tag Manager and enhancing your website’s data collection capabilities.
Watch our Google Tag Manager tutorial series to walk through the steps, and continue reading to follow along as you get started.
Creating Your Google Tag Manager Account
The first step to using Google Tag Manager is creating your account. This simple process sets the foundation for all your future tag management activities.
1. Sign Up for Google Tag Manager: Visit the Google Tag Manager website and sign in with your Google account. If you do not have a Google account, you’ll need to create one first.
2. Create a New Account: You’ll be prompted to create a new account after signing in. Enter your account name, which is usually your company name, and your country. Click "Continue" to proceed.
3. Set Up a Container: A container holds all your tags. You can think of it like a folder where all your tracking codes are stored. Enter a name for your container, usually your website’s name, and select the "Web" option since we’re setting this up for a website. Click "Create" and review the terms of service. Once you accept, your account and container are created.
4. Install the Code Snippet: Google Tag Manager will provide you with a code snippet after creating your account and container. Copy this code, as you’ll need it to install on your website. This step will be covered in more detail later.
Creating your Google Tag Manager account correctly ensures you’re set up to efficiently manage tags and gather reliable data.
Setting Up Your First Container
After creating your account and container, the next step is to set up your first tag.
1. Add Your First Tag: Inside the container, click on "Add a New Tag" to begin. This will be the tracking code for Google Analytics or any other service you want to use. Click on the "Tag Configuration" section and select the type of tag you’re adding. For instance, to track page views in Google Analytics, select "Google Tag."
2. Configure Your Tag: Enter the necessary information for the tag. For Google Analytics, you'll need your measurement ID. This ID can be found in your Google Analytics property.
3. Set Up Triggers: Triggers define when the tag should fire. For basic setups, you can select "Initialization - All Pages" to ensure the tag fires on every page of your website. More advanced triggers can be set up based on your needs.
4. Save and Publish: After configuring the tag and setting up the trigger, save your tag. Then, click on "Submit" to publish your container. This makes the tags live on your site.
By setting up your first container correctly, you lay the groundwork for efficient and accurate tag management. This ensures that your website’s data collection is both comprehensive and reliable.
Installing the Tag Manager Code on Your Website
Now, it’s time to install the Google Tag Manager code snippet on your website. This is a crucial step to ensure that all your tags work correctly.
1. Locate the Code Snippet: After setting up your container, Google Tag Manager provides two pieces of code. You’ll need to install both on your website. The first snippet goes in the 'head' section of your website, and the second snippet goes immediately after the opening 'body' tag.
2. Access Your Website’s Code: Depending on how your website is built, accessing your website’s code can vary. If you are using a content management system like WordPress, you can use a plugin to add the container code. Otherwise, you can add the code to your theme or template file. We recommend searching the support section for your website platform to view the available options for adding Google Tag Manager.
3. Verify Installation: To ensure the code snippet is installed correctly, go back to Google Tag Manager and click on the "Preview" button. This loads Google Tag Assistant along with your website. You can then navigate through your website and complete other actions to see if your tags are triggered.
Installing the Google Tag Manager container code correctly is critical. Without the container code, you won’t be able to implement your tags.
Configuring Additional Tags
Once the container code is installed and you’ve tested that your first tag is being fired correctly, the next step is to add additional tags. Any tags added directly to your website’s code can potentially be migrated to Google Tag Manager.
Tags you should consider migrating to Google Tag Manager include:
1. Google Ads Tags: This includes Google Ads conversion tags and Google Ads remarketing tags.
2. Third-party Advertising Tags: If you’re advertising with Microsoft, Facebook, and any other platforms, you should consider installing these tags using Google Tag Manager.
3. Third-party Analytics Tags: This might include Microsoft Clarity, Hotjar, Cloudflare Analytics, and any other analytics tags currently being used on your website.
4. Conversion Testing Platforms: If you’re using a testing platform like Crazy Egg or Zoho PageSense, you can look at migrating these tags to Google Tag Manager. However, there are likely to be additional considerations, as testing platforms might need to load before the Google Tag Manager container code.
By carefully configuring and testing your tags, you ensure your data collection is accurate and reliable, providing a solid foundation for your analytics and marketing efforts.
Conclusion
Setting up Google Tag Manager can streamline the management of advertising and analytics tags on your website. It offers a centralized platform to manage all your tags, making deploying and updating them easier without needing to touch your site’s code frequently. Whether you are tracking page views, conversions, or various user interactions, Google Tag Manager is an invaluable tool for enhancing and simplifying your analytics setup.
You can efficiently manage all your website’s tracking needs by following the steps outlined, including creating your account, setting up a container, installing the code snippet, and configuring and testing your tags. Implement these practices to ensure you collect accurate data, which can help you make informed decisions about your online marketing strategies.
To deepen your understanding of digital marketing tools like Google Tag Manager, join our Google Tag Manager Course. Our courses will help you master these tools and take your digital analytics skills to the next level.


Comments